Turbocharger vs. Supercharger: Key Differences Explained
A simple guide comparing turbochargers and superchargers, their pros and cons, and how to choose the right one for your driving style.
When it comes to squeezing more performance out of an engine, two technologies dominate the conversation—turbocharger vs. supercharger. Both are designed to boost power by forcing more air into the combustion chamber, yet the way they achieve it and the driving experience they deliver are quite different. Whether you’re chasing fuel‑efficient speed or raw, instant acceleration, understanding how each system works is key to making the right choice.
In this guide, we’ll break it down and debate in clear, simple terms. You’ll learn how each system operates, its pros and cons, how they feel behind the wheel, and even which models in the UAE use them. By the end, you’ll have the knowledge to decide which one fits your driving style, and why the right choice might just change the way you see performance cars.
How a Turbocharger Works
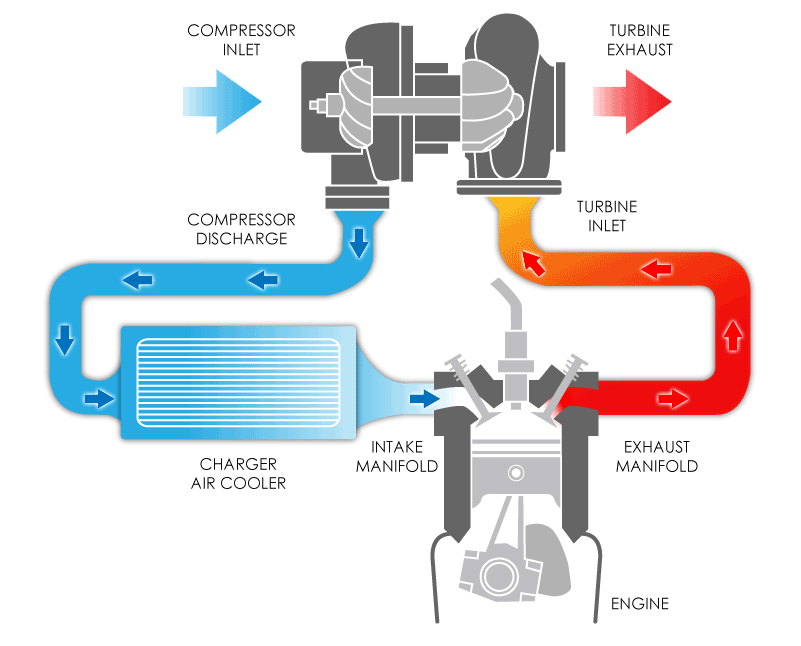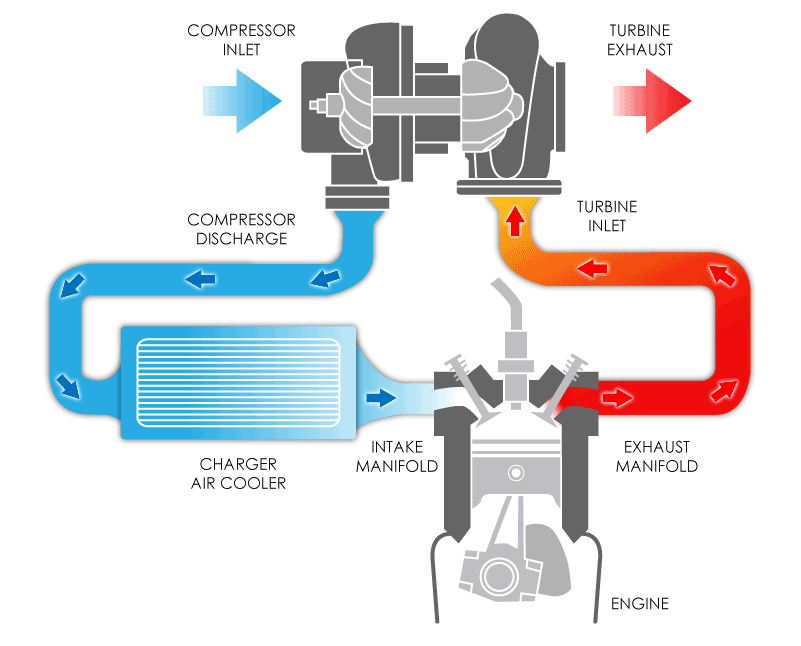
A turbocharger might sound complicated; however, seeing it in action makes the concept much easier to grasp. The diagram below shows how exhaust gases spin a turbine, which in turn compresses fresh air into the engine. This process packs more oxygen into each cylinder, allowing more fuel to burn and generating a bigger burst of power—all without adding extra strain to the engine’s crankshaft.
-
The turbine wheel connects via a shaft to the compressor wheel on the intake side.
-
From there, the compressor wheel draws in outside air and compresses it.
-
Once compressed, the denser, oxygen‑rich air is pushed into the engine’s intake manifold.
Key parts and airflow paths:
-
Exhaust Flow In: Hot exhaust gases exit the engine’s combustion chambers and travel toward the turbocharger.
-
Turbine Wheel: The turbine wheel connects via a shaft to the compressor wheel on the intake side.
-
Shaft Connection: The turbine wheel is connected by a shaft to the compressor wheel on the intake side.
-
Compressor Wheel: From there, the compressor wheel draws in outside air and compresses it.
-
Compressed Air to Engine: Once compressed, the denser, oxygen‑rich air is pushed into the engine’s intake manifold
-
Intercooler (Optional): Many systems send the hot compressed air through an intercooler to cool it before it enters the engine, increasing efficiency and preventing knock.
In short: The turbo recycles exhaust energy to spin a turbine, which compresses fresh air into the engine—boosting power without extra load on the crankshaft.
How a Supercharger Works
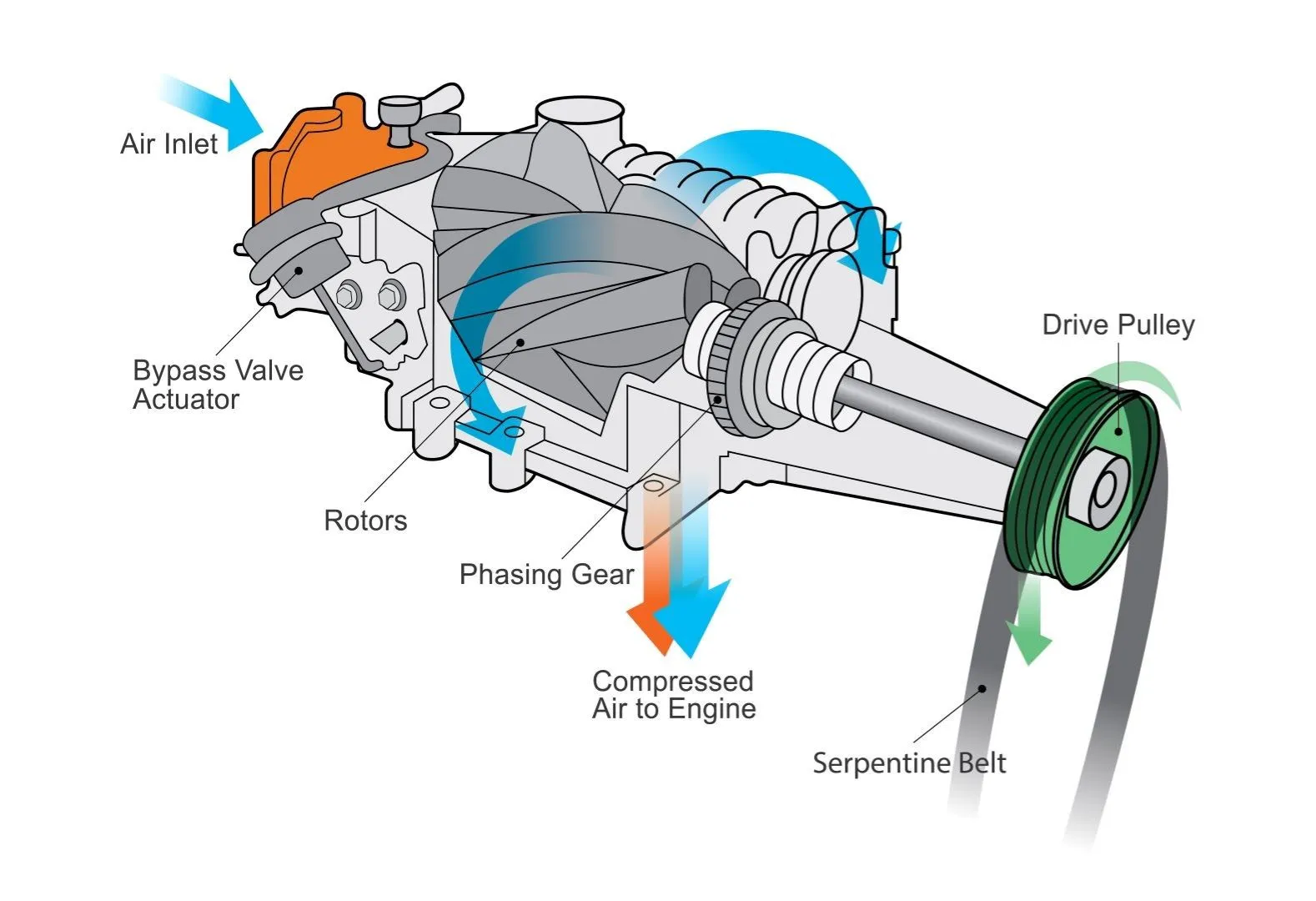
A supercharger takes a more direct approach. Instead of waiting for exhaust gases, it’s powered by a belt connected to the engine’s crankshaft; as a result, power is delivered instantly. The result? Power is delivered instantly—no lag, no waiting.
This makes superchargers a favorite for muscle cars, drag racing, and situations where you want maximum punch the moment you step on the pedal. The downside is that they use engine power to make more power, which can slightly lower fuel efficiency.
Quick facts about superchargers:
-
Belt-driven from the crankshaft
-
Instant boost with no lag
-
Great for low-RPM torque
-
Slightly less fuel-efficient than turbos
Turbocharger vs Supercharger: At a Glance
| Feature | Turbocharger | Supercharger |
|---|---|---|
| Power Source | Exhaust gases | Engine crankshaft |
| Efficiency | More fuel-efficient | Less fuel-efficient |
| Power Delivery | Some lag before boost | Instant boost |
| Installation | More complex | Simpler mechanically |
| Weight | Lighter | Heavier |
| Cost | Often cheaper | Can be more expensive |
Turbocharged Models Available in the UAE
In the UAE, turbocharged engines have seen a significant rise in popularity. In earlier years, drivers preferred large naturally aspirated engines—like 4.0L V6 and 5.0L V8 units—for their smooth performance and long-term reliability.
However, modern automotive trends, stricter emission standards, and rising fuel efficiency demands have shifted the market toward smaller turbocharged engines ranging from 1.5L to 3.0L. These engines deliver equal or greater power compared to older big engines while consuming less fuel and producing fewer emissions.
Today, many UAE buyers choose turbocharged SUVs and sedans for their balance of performance and economy, while performance enthusiasts often opt for high-output twin‑turbo or hybrid‑turbo setups to get the best mix of power and efficiency. Some even produce the distinctive “stu‑stu‑stu” turbo flutter—caused when the throttle closes while the turbo still builds boost—a sound many car lovers enjoy.
Popular Turbocharged Models in the UAE:
- Toyota Land Cruiser 300 (3.5L Twin-Turbo V6)
- Nissan Patrol Nismo (5.6L V8 with Turbo upgrades in the tuning market)
- BMW X5 M50i (4.4L twin‑turbocharged V8)
- Mercedes‑AMG A35 (2.0L turbocharged inline‑4)
- Audi RS Q8( 4.0L twin‑turbocharged V8)
Example:
Imagine you’re riding a bicycle downhill. Instead of letting the wind pass by, you attach a small windmill to your bike that spins as you move. The spinning windmill powers a fan that blows extra air into your lungs, helping you pedal faster without using more of your own energy. That’s basically what a turbocharger does—only instead of wind, it uses your car’s exhaust gases to spin a turbine, which forces more air into the engine for a stronger burst of power.
Supercharged Models Available in the UAE
While turbochargers dominate most modern lineups, superchargers still hold strong appeal among UAE buyers who want instant throttle response and raw acceleration. In earlier years, supercharged V8 engines were a status symbol in high‑end SUVs and performance sedans, offering unmatched low‑RPM torque. Today, luxury and performance brands use them in either pure form or paired with turbos for a twin‑boost effect.
Though less fuel-efficient than turbos, superchargers remain popular among driving enthusiasts who prioritize immediate power over economy. Their immediate power delivery and signature high‑pitched “whine”—produced as air is rapidly compressed—keep them popular among driving enthusiasts.
Popular Supercharged Models in the UAE:
- Dodge Charger SRT Hellcat (6.2L supercharged HEMI V8)
- Range Rover Sport SVR (5.0L supercharged V8)
- Jaguar F‑Type R (5.0L supercharged V8)
- Cadillac CTS‑V (used market 6.2L supercharged V8)
Example:
Imagine you’re riding that same bicycle, but this time you have a friend running next to you with an air pump. Every time you pedal, your friend pushes fresh air directly into your lungs through the pump—instantly helping you pedal faster. That’s how a supercharger works. Instead of waiting for exhaust gases like a turbocharger, it’s mechanically connected to the engine’s crankshaft, pushing more air in as soon as you hit the accelerator. The result? Instant power, no delay.
Turbocharger vs. Supercharger: Pros and Cons
| Category | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Turbocharger |
|
|
| Supercharger |
|
|
How They Feel Driving
Behind the wheel, the difference is easy to notice:
-
Turbocharged cars can feel calm at low speeds; however, they suddenly surge forward when the boost arrives.
-
Supercharged cars feel ready to go the moment you tap the accelerator, making them great for quick bursts of speed or confident overtakes.
That’s why you’ll often find turbos in sporty sedans aiming for fuel economy and top-end performance, while superchargers are popular in cars built for raw, instant power.
Twincharging: The Power Combo
Some high-performance cars use both—a setup called twincharging; in this way, drivers get the benefits of both systems. The supercharger handles low-RPM boost, and the turbocharger kicks in at higher speeds. It’s the best of both worlds, but it’s more complex (and more expensive) than choosing one system.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Which is better for daily driving?
Turbochargers are usually better for fuel efficiency; superchargers give instant power.
2. Do turbos need more maintenance?
Yes, due to higher heat and speed. Superchargers are simpler but still need care.
3. Can I add one to any car?
Not always—engine compatibility and proper tuning are essential.
4. Is turbo lag still a problem?
Modern tech has reduced it, but superchargers remain instant.
5. Which costs more?
Superchargers are often pricier, but high-end turbos can also be expensive.
Final Thoughts
In the turbocharger vs. supercharger debate, there’s no single winner—it all depends on your driving style. Turbochargers offer efficiency, modern tuning potential, and strong top‑end power, while superchargers deliver instant throttle response and powerful low‑RPM torque.
If you want smooth cruising with extra speed when needed, a turbo may suit you best. For aggressive, immediate performance, a supercharger is hard to beat. Test-driving both is the best way to see which one truly makes you smile. For more expert comparisons, visit ArabWheels Blogs.